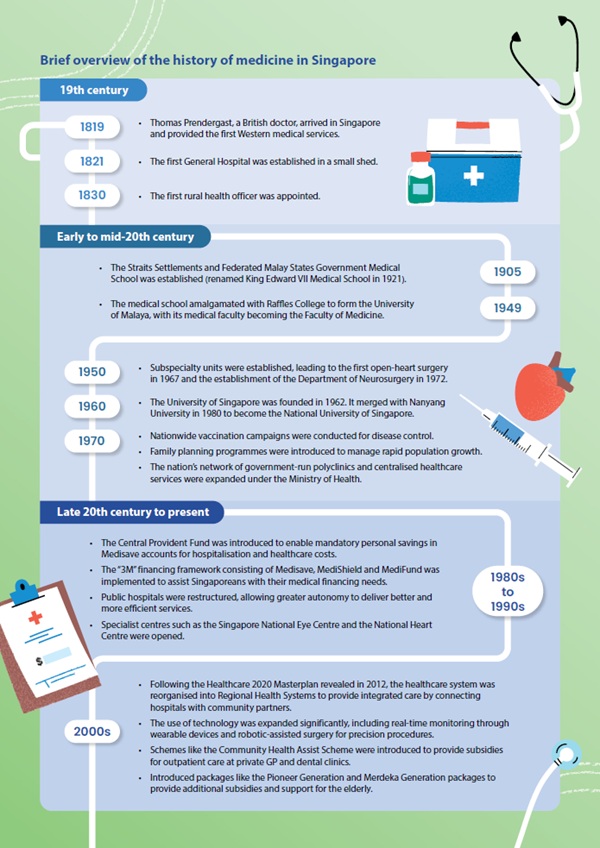
I wanted to see what a chatbot's perspective of the history of medicine in Singapore might be when I was preparing this article, so I asked Google AI Overviews to summarise the history of medicine in Singapore, as well as to tell me about medicine in Singapore in the past 60 years. These paragraphs were what I got in response, each followed by a timeline of events.
"Singapore's medical history began with colonial doctors treating Europeans and the military in the early 19th century, while locals relied on traditional healers. Organised public health efforts started in the late 1830s, leading to the establishment of Singapore's first medical school in 1905, which later became the King Edward VII College of Medicine and eventually the Faculty of Medicine at the National University of Singapore (NUS). Post-independence, the focus shifted to developing a robust, publicly financed healthcare system with elements of social risk-pooling through schemes like Medisave and Medishield Life."
"Over the past 60 years, medicine in Singapore has transformed from a rudimentary system tackling infectious diseases into a world-class, multi-tiered healthcare system focused on chronic diseases and an ageing population. This progress was driven by strategic government policies, medical breakthroughs and substantial investment in infrastructure."
Although the results were quite brief, it was not too bad. The Google Knowledge Panel told me that the Google AI mode visited ten websites, including SMA News.The generated references included parts 1, 3, 7 and 14 of the 14-part series "A Glimpse into the Past – Medicine in Singapore", published in the newsletter.1,2,3,4
The AI mode's references even included materials that I had forgotten about or had not read before:
Appreciating our history
Is there a need for health professionals to be familiar with the history of medicine? There are various often-cited reasons,10 which include:
- Learning from the past and preventing past mistakes.
- Documenting outstanding events from the past and attributing credit accurately.
- Understanding the context of the evolution of medical and scientific knowledge.
-
Instilling pride and identity.
Personally, why am I interested in the history of medicine?
Firstly, I have a keen interest in the history of science and medicine. The stories of the history of medicine are like the detective stories of Sir Arthur Conan Doyle and Agatha Christie. The unravelling of medical mysteries which fascinate me, to name but two, include:
- Levine and Stetson investigating the mystery of a stillbirth in a woman who received a blood transfusion from her husband,11 and Landsteiner' blood transfusion experiments in the rhesus macaque.12 See Levine's biog raphy (pages 323 to 347) in the downloadable book Biographical Memoirs: Volume 63.13
- The discovery of prion disease: the strange story of scrapie and Merino sheep;14 to the description of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in the 1920s;15 to the 1957 report by Gajdusek and Zigas of the trembling (kuru) disease or laughing death in Papua New Guinea;16 to the 1960s hypothesis of endocannibalism by Matthews, Glasse and Lindenbaum; 17 to Gajdusek's 1976 Nobel Prize and his 1997 imprisonment for child molestation;18 to the coining of the term "prion" in the 1980s19 and Stanley Prusiner's 1997 Nobel Prize.20 Read about the story of kuru, 21 the life of Carleton Gajdusek,22 and the skepticism that Stanley Prusiner faced.23
Secondly, the history of medicine is intertwined with the evolution and development of critical thinking:24 the questioning of tradition, the development of scientific inquiry, professional development, improving healthcare quality and fostering social responsibility. If you have the time, listen to this 90-minute talk: "Making the Case for History in Medical Education" by David Jones, a psychiatrist at Harvard Medical School and Professor of the Culture of Medicine at Harvard University.25
Looking ahead
What of the future of medicine? The future is very exciting; for example, the World Economic Forum mentions expectations of revolutionary advances in precision medicine, artificial intelligence, gene editing, wearable technology, robotics, additive manufacturing, regenerative medicine, healthy longevity, drug discovery, clinical trials planning and execution, medical image recognition, automated document processing, electronic health records interoperability, supply chain augmentation and supply chain risk assessment, public health surveillance, and resource allocation.26